Chances are you have had an x-ray in the past. Maybe you fell off a swing or trampoline when you were a child. Most people have heard of a CT scan, MRI or ultrasound (US) but may have not had one.
Read further to find out what each scan is, what it’s used for, and when you may be asked to get one.
X-Ray:
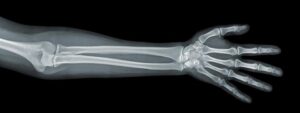
Used to check bone fractures or breaks
Pros:
• Cost effective $$
• High level of success for fractures $$
• Quick and easy, usually does not require booking$$
• Don’t always need a referral (depends on the radiology center)
Cons:
• Radiation: x-rays use radiation which sometimes may be not worth the risk. Don’t be concerned if your health practitioner does not want to immediately x-ray because of this!
• Can miss other types of injury – it’s not good at seeing soft tissues!
Ultrasound:
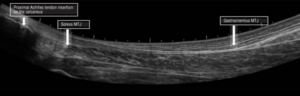
Used to check soft tissue injuries in ligaments or tendons
Pros:
• Most cost effective $
• Quick and easy, usually does not require booking.
• No radiation – ultrasound uses sound waves!
Cons:
• Can easily miss many types of injuries including tendon tears – misdiagnosis can affect long term treatment and recovery
• Is very practitioner dependent – the sonographer must be skilled in using ultrasound to not miss injuries
• Most often used as a baby-step scan before MRI
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) :
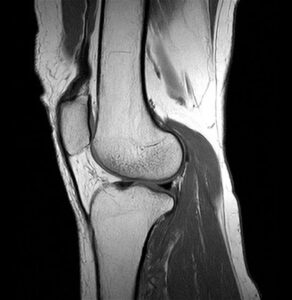
Seen as the “Gold Standard” in imaging in the 21st Century
Used to identify bone, soft tissue and organ injuries such as stress fractures, bone contusion, certain types of dislocation and ligament damage.
Pros:
• Very unlikely to miss an injury
• Can be referred by GP or physiotherapist
• Will show comprehensive image of whole area rather than just bone or soft tissue
• No radiation! MRIs use magnetic fields
• Most often used for diagnosis of ACL rupture
Cons:
• Expensive $$$
• Can be difficult to get an appointment – not all radiology centers have MRI machines
• Claustrophobia – some MRIs can go for a long time and you’re not allowed to move while it’s on
CT (Computed Tomography):
Used for diagnosis of bone and soft tissues injuries: was used for larger scans before the MRI was introduced
Best used for internal trauma such as internal bleeding
Pros:
• Can create a 3d image from the scan to accurate diagnose and identify injuries
• Mid range cost $$: less expensive than MRI, more expensive than X-ray
Cons:
• Higher amounts of radiation: takes many horizontal x rays and compiles them as cross sections to create the image
• Can be difficult to get an appointment – not all radiology centers will have a CT machine. Also some centers will only accept referral from GP
Imaging is a fantastic diagnostic tool and is always used in conjunction with clinical assessment and diagnosis.
If you have any questions feel free to contact us on 9267 3775